Difference between revisions of "RFID tags"
(→Classifications) |
(→Classifications) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
== Classifications == | == Classifications == | ||
| − | In order for objects to be identifiable through RFID, they have to carry the [[SYSCLS OBJECTWITHRFIDTAG]] classification or (optional) the new [[SYSCLS OBJECTWITHRFIDTAGS]] {{Version/ServerSince|4.4.0}} | + | In order for objects to be identifiable through RFID, they have to carry the [[SYSCLS OBJECTWITHRFIDTAG]] classification or (optional) the new [[SYSCLS OBJECTWITHRFIDTAGS]] {{Version/ServerSince|4.4.0}}. |
The service query used for online searching is [[SYSCLS RFIDTAGSCANQUERY]]. | The service query used for online searching is [[SYSCLS RFIDTAGSCANQUERY]]. | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 14 June 2023
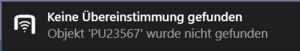
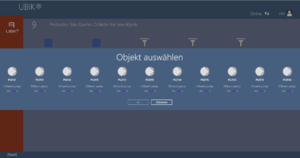
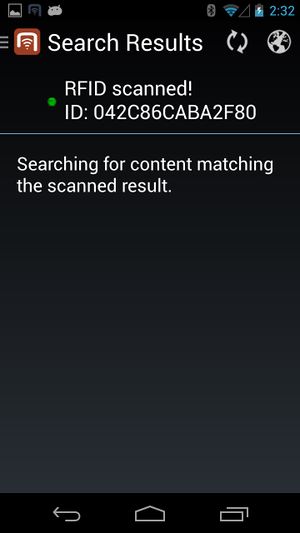
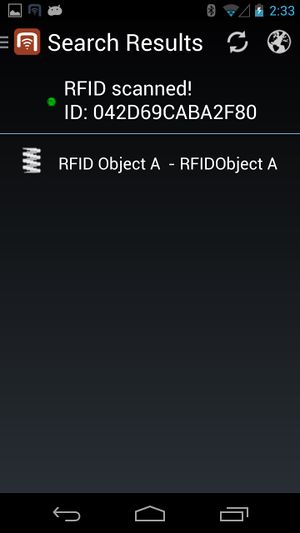
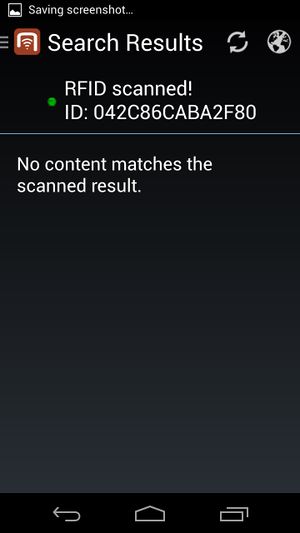
In order for the users to find objects more efficiently, UBIK® objects can be marked with values for RFID/NFC codes. Whenever a user scans an RFID code, the resulting code value can be used to find all matching objects, namely objects that have the right property.
| NFC stands for "Near Field Communication" and is a set of ideas and technologies for data transfer between devices, typically in close distances. Technically, it is based on RFID ("Radio-Frequency Identification"), which describes specific technical solutions. |
Amongst the use cases for NFC, there is communication between smartphones and other devices, but also the scanning of RFID tags.
The UBIK® RFID scanning feature specifically is the ability to scan RFID tags in order to identify UBIK® objects.