Difference between revisions of "HowTo:Use a Query in a View"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A [[QUERY|Query]] object can be shown within a [[VIEW|View]] hierarchy similar to any other object, once the query is placed either as root object of the view or a child of another object shown in the view. | A [[QUERY|Query]] object can be shown within a [[VIEW|View]] hierarchy similar to any other object, once the query is placed either as root object of the view or a child of another object shown in the view. | ||
| − | {{Hint|Be aware that a corresponding [[ | + | {{Hint|Be aware that a corresponding [[QUERYVIEWITEM|View Item]] is necessary for a query as well.}} |
=== Place query among root objects === | === Place query among root objects === | ||
Latest revision as of 11:04, 24 March 2015
A Query object can be shown within a View hierarchy similar to any other object, once the query is placed either as root object of the view or a child of another object shown in the view.
| Be aware that a corresponding View Item is necessary for a query as well. |
Place query among root objects
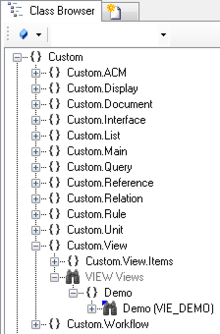
- Navigate to the MetaClass VIEW in the Class Browser.
- To see now the entire structure in the View Test Environment, locate an existing View, nor the required Root objects must be added to view with the Relation Editor.
- Connect a View object to the Relation Editor
- The query object needs to be added to the list of root objects, there are two different ways to achieve that:
- Individual objects can be added directly to the Root object relation of the View using the Relation Editor.
- To add multiple query objects, another Query has to be created and added to the Root query relation in the View.
- Save the changes with Ctrl+S or the save command
| Only the objects which are located directly underneath the Infrastructure relation will be part of the infrastructure. Their child objects will NOT be included (automatically). |