Entity Data Model
Contents
Introduction
Objectives
In an industrial environment we quite often need to
- describe an industrial plant consisting of a bunch of different parts, each having a certain purpose and set of properties, and which are related in various ways
- manage process or maintenance data of the plant and its features
- do a high-performance cost-benefit analysis and create key performance indicators
Therefore we need to
15 px „Dissemble“ the system into theoretical blocks representing the real as well as intangible parts of the system.
15 px Identify the necessary properties of the blocks.
15 px Think about how blocks are possibly related to each other.
15 px Think about the functions and features of blocks.
Plant picture
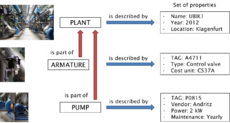
Lets start with a simple picture and assume that our plant consists of a pump and an armature. Both equipments exhibit certain technical or other properties, which our datamodel must contain in some form. Additionally the datamodel has to provide mechanism to indicate the circumstances that both equipments are parts of the plant and maybe even be related to each other. For our first example plant, the pump and armature we find the following definitions
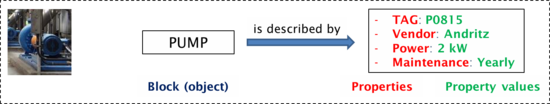
Looking closer at the "PUMP" block reveals its properties and property values
Of course, a real plant consists of multiple pumps, each described with the same set of properties (TAG, vendor, power, maintenance data). The real pumps in the plant are distinguished by different property values as given in the table.
| Pump | TAG | Vendor | Power | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | P0815 | Andritz | 2 kW | Yearly |
| #2 | P0816 | Andritz | 5 kW | Monthly |
| #3 | P0817 | Sulzer | 4 kW | Yearly |
We can redefine or extend our objectives by
15 px
Design a descriptive model including all required blocks and properties of the system
15 px An object in this model specifies possible properties for a certain part of the real system
From the plant picture to UBIK
Transition
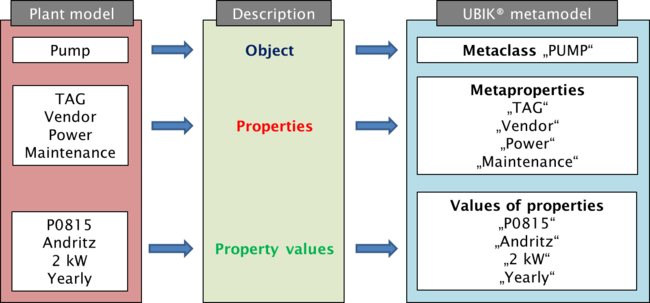
In summary we can picture the transition from the plant picture into an object- / data-model like
and post our first definition
- UBIK metamodel
- A descriptive model, where objects provide information about the aspects of the data, is also called “Metamodel”.
So far we have identified
20 px Theoretical blocks representing the parts of the system
20 px Necessary properties of these blocks
An important aspect of the datamodel has not been discussed yet, namley
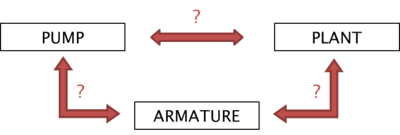
20 px How are the blocks (=metaclasses) related to each other?
Relating objects
Assuming that all three pumps are clearly parts of the plant „UBIK1“, the descriptive model has to be extended in order to include this information as well. In our "table" view we account for this by adding a property to the „Pump“ block refering to the plant. This additional property represents the link information between the pumps #1 - #3 and the plant „UBIK1“.
 |
20 px |
|
- UBIK metamodel
- Add a metaproperty „Plant“ to the metaclass „Pump“, where the values of the metaproperty refer to the plant „UBIK1“.
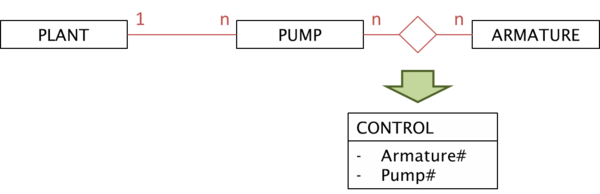
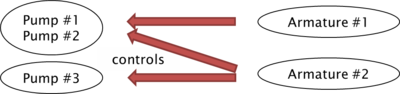
Now we introduce two armatures with the properties from the descriptive model above. Assume that, due to the piping, pumps #1 and #2 are controlled by both armatures, whereas A200 regulates pump #3 only. This situation is depicted below already indicating, that the implementation of the relation requires a more complex structure. We find three pumps on the left side and two armatures on the right side of the relation, respectively. Managing this control relation in the metamodel requires to introduce a relation block „CONTROL“ with two metaproperties „Armature#“ and „Pump#“
 |
20 px |
|
20 px | 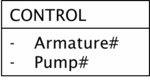 |
- UBIK metamodel
- Managing the control relation in the metamodel requires to introduce a relation block „CONTROL“ with two metaproperties „Armature#“ and „Pump#“.
Lets have a closer look at the characteristics of the two methods relating objects:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 px | 40 px | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| each pump refers exactely to the one plant | two pumps are controlled by two armatures one pump is controlled by one armature |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 px | 40 px | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardinality 1 : n | Cardinality n : n |
- UBIK metamodel
- Data model built and described by metaclasses and metaproperties related to each other, either by 1 : n or n : n cardinality.
Entity Relationship Model (ER model)
In software engineering, such an abstract descriptive model is called Entity–Relationship model (ER model) and describes the entities (=UBIK® metaclasses) and relationships between them. Usually this information is depicted in an entitiy-relationship-diagram (ERD), which draws the corresponding data objects and relations as rectangles and lines between them, respectively.
The metaclass „CONTROL“ can be drawn as diamond, signalling the additional block between these two metaclasses, which is always needed for each relation of cardinality n : n.
About References and Relations
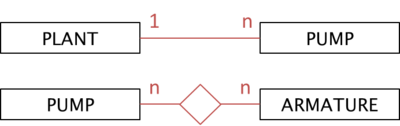
Concluding and summarizing the above discussion we finally depict two possible types of relation in the UBIK metamodel:
- UBIK metamodel
- 1 : n relationships are called “References” (one pump refers to exactly one plant)
- n : n relationships are called “Relations” (two pumps are controlled by two armatures, one pump is controlled by one armature)
Congratulations, we integrated another important issue in our data- and object model:
20 px Relationships between blocks (metaclasses)