Difference between revisions of "Activity:CreateOLEQueryScope (Activity)"
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
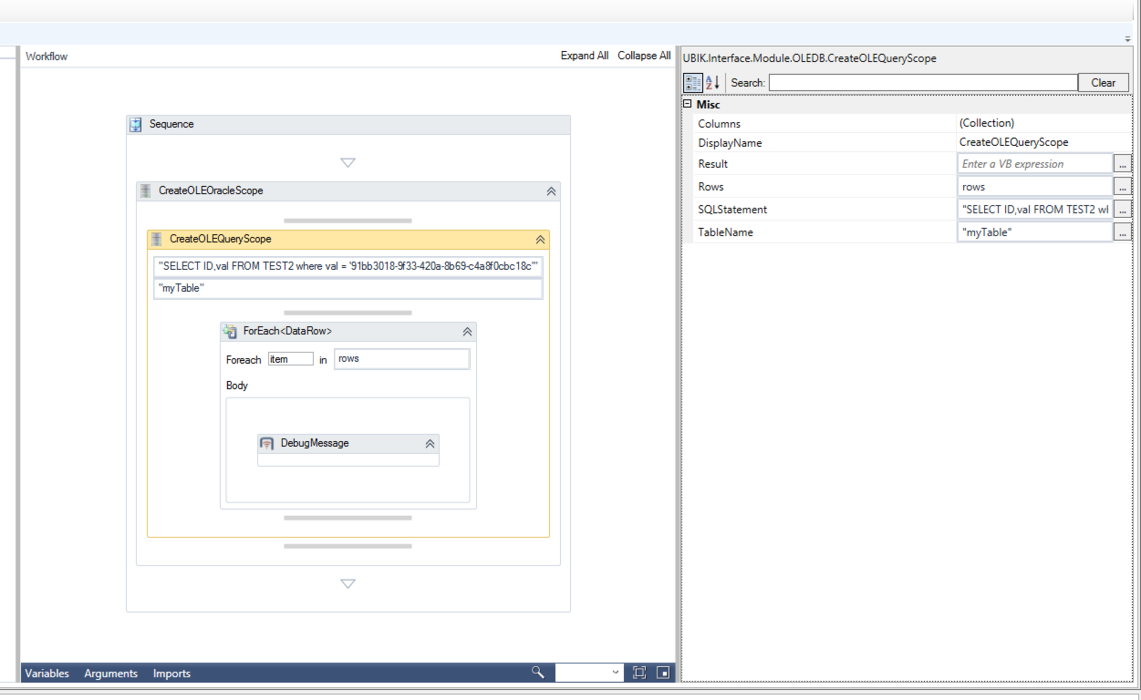
The CreateOLEQueryScope activity, as used in the larger example "Read MetaClass names from UBIK database": | The CreateOLEQueryScope activity, as used in the larger example "Read MetaClass names from UBIK database": | ||
| − | [[File:UI_Activity_CreateOLEQueryScope. | + | [[File:UI_Activity_CreateOLEQueryScope.PNG|x700px]] |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 13:09, 26 January 2015
| Create OLE Query Scope | |
|---|---|
| Name | CreateOLEQuery |
| Purpose | Access database data via OLE |
| Category | UBIK Data Exchange |
| Returns | True if successful |
| Version | 2.4.1+ |
The CreateOLEQueryScope Activity provides access to a tables/views within an OLE compliant database by defining a SQL statement. It is typically nested within a CreateOLEDBScope Activity.
Contents
Arguments
| Argument | Type | Direction | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayName | String | In | The display name of the activity |
| Tablename | String | In | The unique tablename of the statement |
| SQLStatement | String | In | The database statement |
| Rows | IEnumerable<DataRow> | Out | A list of all rows of the table |
| Result | Boolean | Out | True if successful, false if failed |
Usage
This activity is used to access a table(s) or view(s) within a valid OLE DB Scope. The data access is defined by a dtabase SQL Statement.
Tablename
If you are accessing a single table with the statement (example: SELECT * FROM TABELE1), then the table name is optional. In the case of a more complex statement where you include more than one table (example: SELECT * FROM TABELE1, TABELE2 where TABELE1.PK = TABELE2.pk ....) then you have to define a unique tablename defining the access indicator for the OLE system.
Example
The CreateOLEQueryScope activity, as used in the larger example "Read MetaClass names from UBIK database":