Difference between revisions of "USAM"
(→LAS (Local Application Service)) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''U'''BIK '''S'''ession '''A'''uthentication '''M'''anagement (USAM) is a mechanism for managing all connected users logged in to one or more {{UBIK}} databases. There are three modes of session authentication: Single Local Application, '''L'''ocal '''A'''pplication '''S'''ervice (LAS) and '''G'''lobal '''A'''pplication '''S'''ervice (GAS). | The '''U'''BIK '''S'''ession '''A'''uthentication '''M'''anagement (USAM) is a mechanism for managing all connected users logged in to one or more {{UBIK}} databases. There are three modes of session authentication: Single Local Application, '''L'''ocal '''A'''pplication '''S'''ervice (LAS) and '''G'''lobal '''A'''pplication '''S'''ervice (GAS). | ||
== Single Local Application == | == Single Local Application == | ||
| − | This means that no explicit authorization mechanism is used. The user's session is a single session which cannot be terminated by another user or the system itself. See how to [[Configure Single Local Application Authentication|configure authentication using Single Local Application]]. | + | This means that no explicit authorization mechanism is used. The user's session is a single session which cannot be terminated by another user or the system itself. See how to [[HowTo:Configure Single Local Application Authentication|configure authentication using Single Local Application]]. |
[[File:USAM_SingleLocal.png|alt=Single Local Application|Single Local Application]] | [[File:USAM_SingleLocal.png|alt=Single Local Application|Single Local Application]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== GAS (Global Application Service) == | == GAS (Global Application Service) == | ||
| − | GAS means the session management is managing connections for one or more databases via a separate database used to manage these sessions. A client has to be configured to use the session management service address for athentication and to use a different data service address. See how to [[Configure GAS Authentication|configure authentication using GAS]]. | + | GAS means the session management is managing connections for one or more databases via a separate database used to manage these sessions. A client has to be configured to use the session management service address for athentication and to use a different data service address. See how to [[HowTo:Configure GAS Authentication|configure authentication using GAS]]. |
[[File:USAM_GAS.png|alt=Global Application Service|Global Application Service]] | [[File:USAM_GAS.png|alt=Global Application Service|Global Application Service]] | ||
Revision as of 15:33, 27 January 2015
The UBIK Session Authentication Management (USAM) is a mechanism for managing all connected users logged in to one or more UBIK® databases. There are three modes of session authentication: Single Local Application, Local Application Service (LAS) and Global Application Service (GAS).
Contents
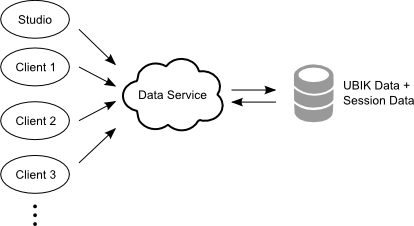
Single Local Application
This means that no explicit authorization mechanism is used. The user's session is a single session which cannot be terminated by another user or the system itself. See how to configure authentication using Single Local Application.
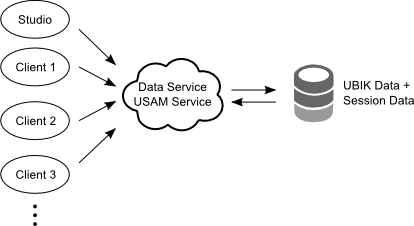
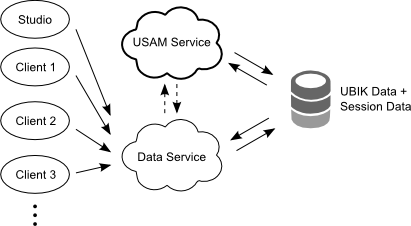
LAS (Local Application Service)
When a LAS is used, the session management service and the data service share one database connection. This does not mean that a local authentication service has to be in the same location as the data webservice, only the database connection for both services have to be configured to use the same connection. See how to configure authentication using LAS.
LAS using one web service location
LAS using different web service locations
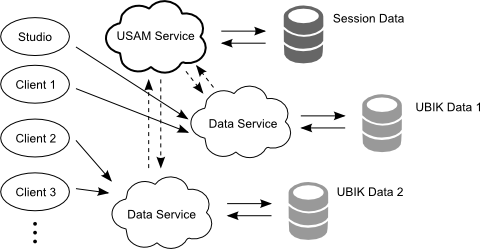
GAS (Global Application Service)
GAS means the session management is managing connections for one or more databases via a separate database used to manage these sessions. A client has to be configured to use the session management service address for athentication and to use a different data service address. See how to configure authentication using GAS.