Difference between revisions of "HowTo:Install UBIK Web Service"
(→Additional prerequisites) |
(→Testing the new service) |
||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
* Ensure that port forwarding is established if needed (e.g. for Microsoft Azure Virtual Computers or servers behind a gateway) | * Ensure that port forwarding is established if needed (e.g. for Microsoft Azure Virtual Computers or servers behind a gateway) | ||
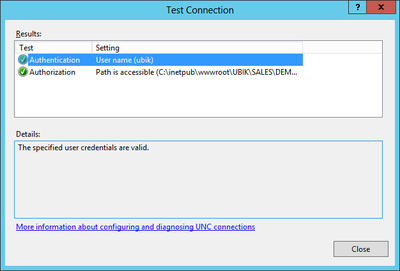
| − | + | == Testing the new service == | |
[[File:UI Test New Service.01.png|600px|border|alt=01 Test New Service|01 Test New Service]] | [[File:UI Test New Service.01.png|600px|border|alt=01 Test New Service|01 Test New Service]] | ||
Revision as of 09:48, 5 June 2014
This page describes how to set up a UBIK® web service on a Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) installed on Microsoft Server 2012. The web service is used to publish data from the UBIK® database to a mobile device (eg mobile phone, tablet).
Contents
Installation of Microsoft IIS
Install server role
Start the server manager to install the Internet Information Services (IIS) on Windows Server 2012 by
- Clicking the Windows Start button, point to Administrative Tools and choose Server Manager
- Clicking on Roles Summary
- Clicking on Add Roles
- Use the Add Roles wizard to add the web server role
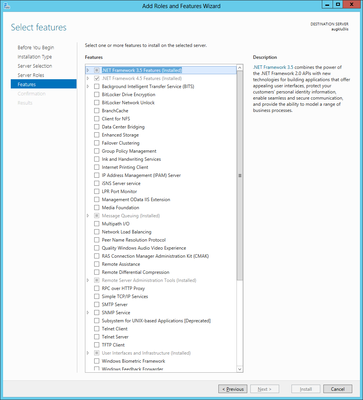
Required roles and features
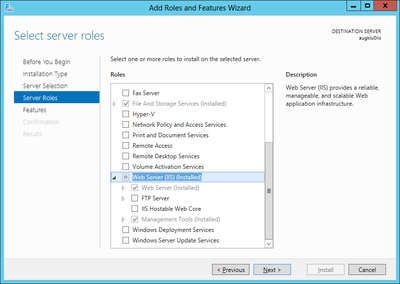
The Add Roles wizard installs only the default set of role services, which do not contain all the necessary features required for UBIK® web services. Therefore, additional IIS role services and features, such as Application Development or Health and Diagnostics, needs to be selected in the Select Role Services page of the wizard.
UBIK® web service requires at least the following roles
- Microsoft .NET Framework 4
- Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5
- Webserver Application Development
and features
- HTTP Actication (WCF Services)
Using a virtual server
A physical server with Microsoft Server 2012 can be used as the host system as well as a virtual server. Use Hyper-V to install and operate serveral virtual servers and proceed with the web server installation similar as for a physical server.
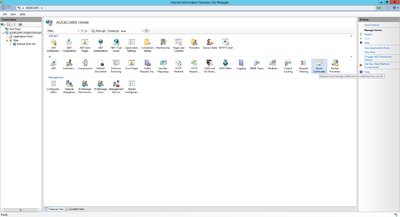
Configuration of the Web Server
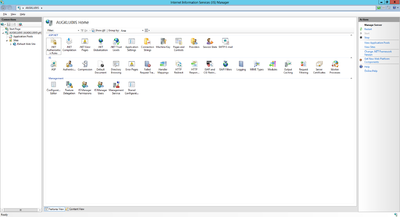
The web server can be configured using the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager console, which gets installed automatically. The console provides a graphical user interface to manage and configure the web server accordingly to the UBIK® web service.
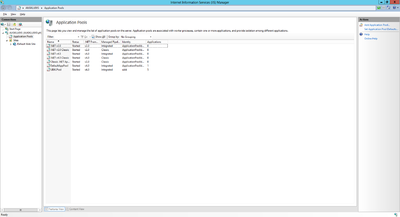
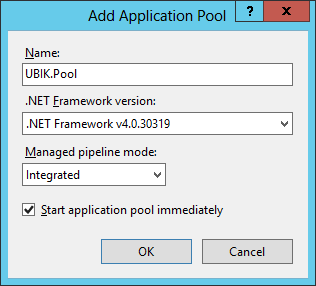
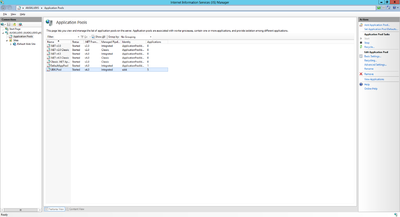
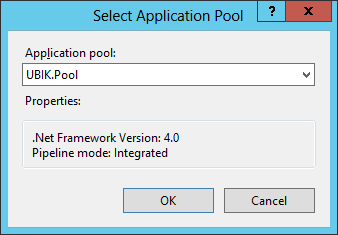
Add Application Pool
An application pool is a group of one or more URLs that are served by a worker process or a set of worker processes. Application pools set boundaries for the applications they contain, which means that any applications that are running outside a given application pool cannot affect the applications in the application pool.
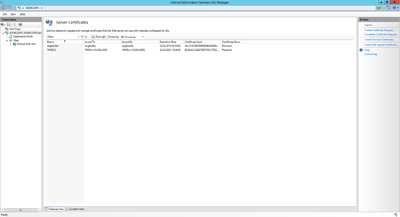
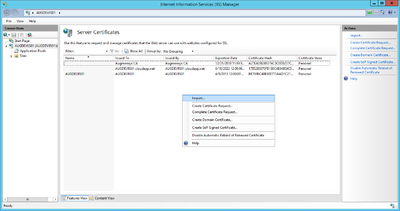
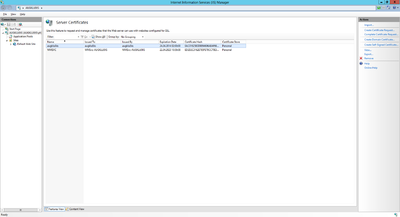
Certificate
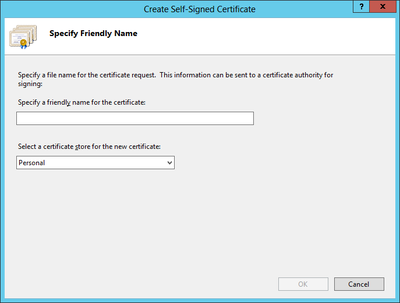
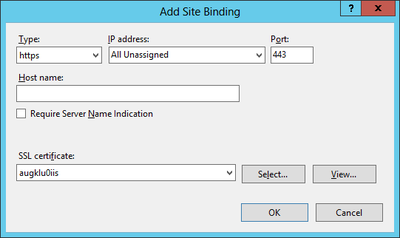
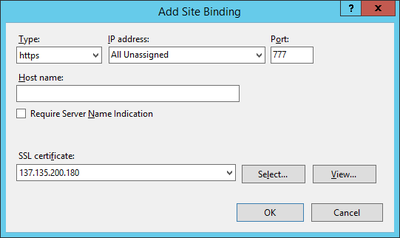
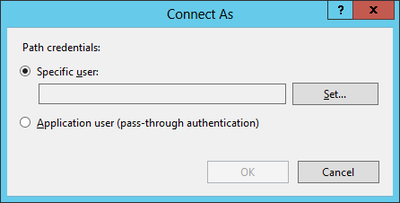
The web service communicates with the UBIK® client via an secured connection, which requires a SSL certificate on the server and client side. Use a public key certificate from a certificate authority or a self-signed certificate, both will work for UBIK®. A new self-signed certificate can be created in the Internet Information Server (IIS) Manager, exported using the export function and sent to the development team. As already mentioned, the client has to know this certificate as well, hence it need to be integrated it into the mobile application.
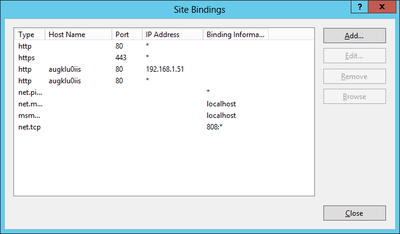
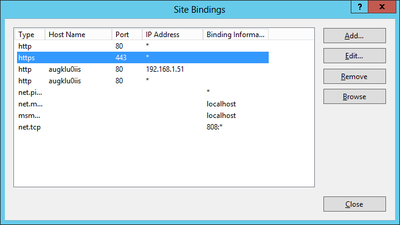
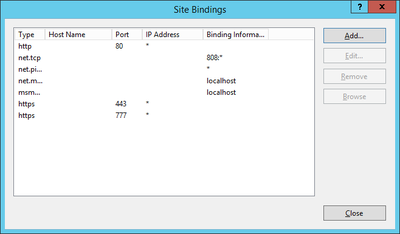
Bindings
Web sites and services have something called Server Bindings which represent the underlying address, port, and potentially a host header that the website is accessed using. The UBIK® client accesses the web service via a secured port (https), where it is necessary to configure the appropriate certificate.
For Android Clients
For Windows 8.1 Clients
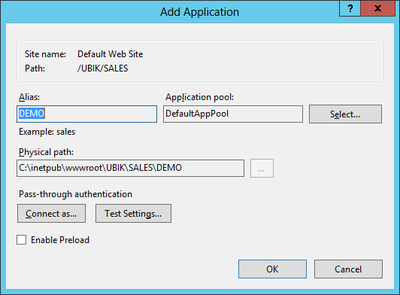
Create new Web Application
In the IIS Manager expand the Default Web Site node and navigate through the folder structure to the folder containing the UBIK® web service components.
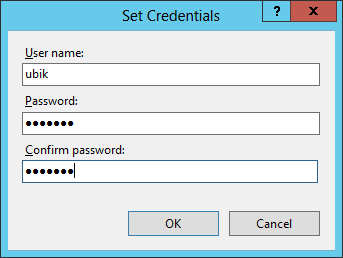
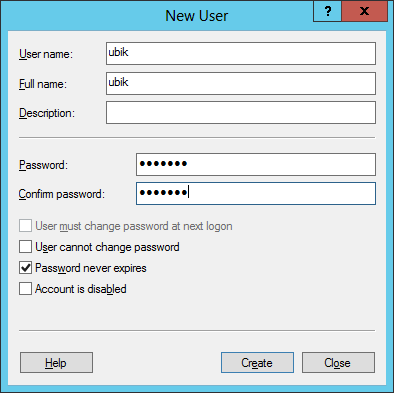
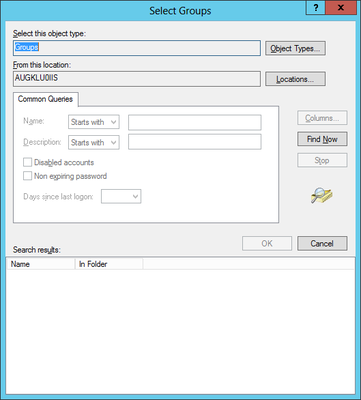
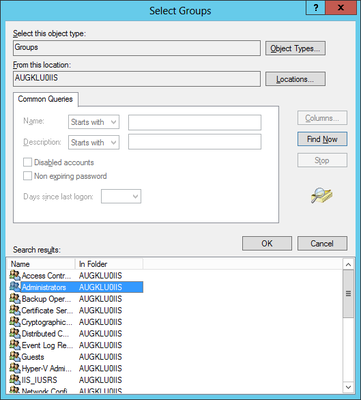
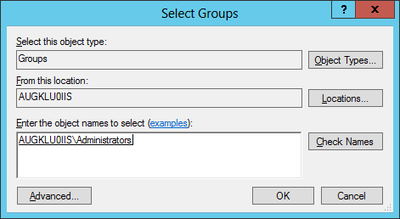
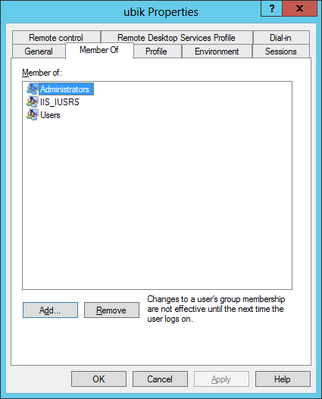
Optional: Local IIS User
Create and use a local user on the web server if no appropriate domain-user is available.
Additional prerequisites
- Ensure that the service ports are not blocked by a firewall.
- Ensure that port forwarding is established if needed (e.g. for Microsoft Azure Virtual Computers or servers behind a gateway)