Difference between revisions of "HowTo:Configure Dynamic AR Content"
(→Action Setup) |
(→Example) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
= Prerequisites = | = Prerequisites = | ||
| − | In order to be able to use the feature properly, a certain folder structure is required and can be found at the following link | + | In order to be able to use the feature properly, a certain folder structure is required and can be found at the following link {{FileLink|Dynamic_AR_Content_Folder_Structure.rar|Dynamic_AR_Content_Folder_Structure.rar}}. Since version 2.4.4, the schema changed slightly (downwards compatible). The updated example package can be found here: {{FileLink|Dynamic_AR_Content_Folder_Structure_244.zip|Dynamic_AR_Content_Folder_Structure_244.zip}} |
| + | The setup folder contains: | ||
# A root folder, named ''UBIK'' | # A root folder, named ''UBIK'' | ||
# The ''UBIK'' root folder contains a child folder, named ''ARConfig'' | # The ''UBIK'' root folder contains a child folder, named ''ARConfig'' | ||
| Line 61: | Line 62: | ||
= Action Setup = | = Action Setup = | ||
| − | After the folder is configured, the next step is to validate the schema against an online validator. A solution can be found at [http://www.utilities-online.info/xsdvalidation/ Online XML Schema Validator]. The schema used to validate against can be found inside the | + | After the folder is configured, the next step is to validate the schema against an online validator. A solution can be found at [http://www.utilities-online.info/xsdvalidation/ Online XML Schema Validator]. The schema used to validate against can be found inside the example package provided in the prerequisites section (xml_schema_xsd). |
| + | Since version 2.4.4, GeometryAction derives from UBIKObjectAction. When a geometry is clicked, it will try to find the respective UBIK object and show a dialog for it. | ||
The action mapping Xml contains different actions such as | The action mapping Xml contains different actions such as | ||
| Line 72: | Line 74: | ||
<TrackingActionMapping> | <TrackingActionMapping> | ||
<GeometryAction TrackingID="1"> | <GeometryAction TrackingID="1"> | ||
| + | <!-- Since 2.4.4, you can use a UBIK-UID for linking an POI dialog to the geometry. --> | ||
| + | <!-- Alternatively, you can configure (by customizing) an object with Marker Classification and its Marker ID set to the Tracking ID of this action. --> | ||
| + | <UBIK-UID>a5aa5a70-591f-11e3-949a-0800200c9a66</UBIK-UID> | ||
<GeometryResource> | <GeometryResource> | ||
<ResourcePath>pump.obj</ResourcePath> | <ResourcePath>pump.obj</ResourcePath> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 94: | ||
<UBIKObjectAction TrackingID="3"> | <UBIKObjectAction TrackingID="3"> | ||
| + | <!-- Alternatively, you can configure (by customizing) an object with Marker Classification and its Marker ID set to the Tracking ID of this action. --> | ||
<UBIK-UID>a5aa5a70-591f-11e3-949a-0800200c9a66</UBIK-UID> | <UBIK-UID>a5aa5a70-591f-11e3-949a-0800200c9a66</UBIK-UID> | ||
</UBIKObjectAction> | </UBIKObjectAction> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 108: | ||
3D objects can be displayed using the ''<GeometryAction>'' tag. The sub-tag ''<GeometryResource>'' defines the content and the parameters for displaying the 3D object. | 3D objects can be displayed using the ''<GeometryAction>'' tag. The sub-tag ''<GeometryResource>'' defines the content and the parameters for displaying the 3D object. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== UBIK-UID Tag ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Available since version 2.4.4: | ||
| + | Just like the UBIKObjectAction, this action allows the usage of a optional UBIK-UID tag, specifying the ID of a UBIK object. | ||
| + | If it is specified, the respective object is linked to this geometry; else, it is tried to find an object with a marker classification and the geometry action's tracking ID for it's marker id value. | ||
| + | When the user clicks on the geometry, a dialog is opened for the linked object (if found). | ||
==== GeometryResource Tag ==== | ==== GeometryResource Tag ==== | ||
| Line 169: | Line 182: | ||
=== ID Marker Activity === | === ID Marker Activity === | ||
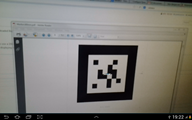
| − | The | + | The ID markers used can be found at the following link {{FileLink|ID_Marker_Example_1_6.pdf|ID Marker Example Ids 1-6}}.<br> |
| − | Having in mind the setup tracking | + | Having in mind the setup tracking IDs, you can now scan ID markers. |
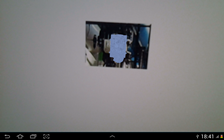
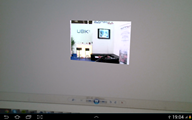
| − | * For an | + | * For an ID that has a 3D object mapped in the action xml, the object should be displayed on the screen as shown in the next picture. |
| − | * If the | + | * If the ID has a video object mapped in the action xml, you should see a video object on the screen, depending on the existence of the play button. Clicking the play button starts the video. |
* If the play button exist you should see first see the play button, and after it's clicked the mapped video. If the play button doesn't exist, a movie preview image will be shown. Clicking the image starts the video. | * If the play button exist you should see first see the play button, and after it's clicked the mapped video. If the play button doesn't exist, a movie preview image will be shown. Clicking the image starts the video. | ||
=== Markerless Activity === | === Markerless Activity === | ||
| − | The markerless photos used in this example can be found at the following link | + | The markerless photos used in this example can be found at the following link {{FileLink|Markerless_Examples._Pics_1-7.pdf|Markerless example pictures}}.<br> |
| − | The scenario is very similar with the | + | The scenario is very similar with the ID marker activity with the only difference that instead of IDs you have to scan your tracking images. |
=== Results === | === Results === | ||
| Line 200: | Line 213: | ||
:[[File:scanning_id6_movie.png|border]] <br> | :[[File:scanning_id6_movie.png|border]] <br> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Client|Configure Dynamic AR Content]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:How-To|Configure Dynamic AR Content]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:POI|Configure Dynamic AR Content]] |
Latest revision as of 09:28, 20 May 2015
The Dynamic AR Content feature allows the user to see different content according to a marker configuration. The configurable content are 3D objects, movies and UBIK® objects. Currently this feature is enabled for ID Markers and Markerless scanning, meaning image tracking. Therefore, every time the user has scanned an ID marker or a picture, the corresponding object (3D object, movie or UBIK® object) will be processed and, according to the configuration, displayed on the screen.