Difference between revisions of "QUERY"
(→Content query) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Content query == | ==Content query == | ||
| + | Objects can be loaded on demand from the server, as storing a huge amount of data permanently on the device would need too much resources. | ||
| + | A content query needs to be | ||
| + | * an [[QUERY]] instance classified as [[SYSCLS_QUERY]] | ||
| + | * related either to other content objects (to show up somewhere in the view hierarchy) or placed as root object of a [[VIEW|View]] | ||
| + | * described by a [[QUERYSCOPE|Query Scopes]] in the ACM | ||
| − | + | Further it is nessary to | |
| − | + | * create a [[QueryViewItem|HowTo:Create_a_new_ViewItem]] for the query object itself | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
* Set filter object (FILTEROBJECT) similar as for other query | * Set filter object (FILTEROBJECT) similar as for other query | ||
* Create a proper relation | * Create a proper relation | ||
| Line 43: | Line 39: | ||
* Create and relate a query context scope and set the instance as QUERY | * Create and relate a query context scope and set the instance as QUERY | ||
* For the scope define the MetaProperties, which should be available as filter criteria on the client. Without appropriate query item, equality is used as filter operator (=) | * For the scope define the MetaProperties, which should be available as filter criteria on the client. Without appropriate query item, equality is used as filter operator (=) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Once the scan is finished, wait until the scanner is closed and an empty browser shows up; | ||
| + | # Depending on the network connection and the {{UBIK}} [[Sync Mode|sync mode]], [[Optical code#Searching for objects|different ways of searching]] will be applied; | ||
| + | # During the search, the list might show a searching text before any objects are found;<br/>[[File:UI_Android_SearchObjectWithOpticalCode.jpg|420 px|border|alt=Searching for Objects|Searching for Objects]] | ||
| + | # If any objects are found, they will be added to the list.<br/>[[File:UI_Android_ObjectWithOpticalCodeFound.jpg|420 px|border|alt=Displaying Objects|Displaying Objects]] | ||
== Scan query == | == Scan query == | ||
Revision as of 11:39, 24 March 2015
| Name | QUERY |
|---|---|
| Namespace | System.Query |
| Internal Name | SystemObjects.QUERY |
| TypeString | UBIK.Kernel.MetaClass |
| RuntimeType | UBIK.Kernel.Query |
| Purpose | Configure queries |
| Version | 2+ |
In UBIK, queries are used for fetching a list of ContentClasses from the database. Queries use data base mechanism for perfomant data access and will deliver a list of objects of a certain Metaclass. Queries can be used in different scenarios:
- data fetching (n records)
- finding a single or a set of recordset(s)
- used as definition of root nodes in a View
| There are specific methods available for this type! |
Contents
[hide]Query and QueryItems
A Query is defined for a single MetaClass, where the MetaClass is defined in the property FILTEROBJECT. Once a query is evaluated it will deliver a list of objects of type ContentClasses (instances), filtered as defined by its QueryItems. The correspondence between Queries and its items is created and stored by a relationship SYSREL QUERY. Therefore a single QueryItem can be used several times for different Queries.
Content query
Objects can be loaded on demand from the server, as storing a huge amount of data permanently on the device would need too much resources.
A content query needs to be
- an QUERY instance classified as SYSCLS QUERY
- related either to other content objects (to show up somewhere in the view hierarchy) or placed as root object of a View
- described by a Query Scopes in the ACM
Further it is nessary to
- create a HowTo:Create_a_new_ViewItem for the query object itself
- Set filter object (FILTEROBJECT) similar as for other query
- Create a proper relation
- Create a query view item and set the instance as QUERY
- Create a relation view item and set the according default MetaClass and relation
- Create and relate a query context scope and set the instance as QUERY
- For the scope define the MetaProperties, which should be available as filter criteria on the client. Without appropriate query item, equality is used as filter operator (=)
- Once the scan is finished, wait until the scanner is closed and an empty browser shows up;
- Depending on the network connection and the UBIK® sync mode, different ways of searching will be applied;
- During the search, the list might show a searching text before any objects are found;
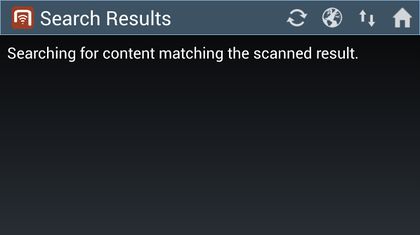
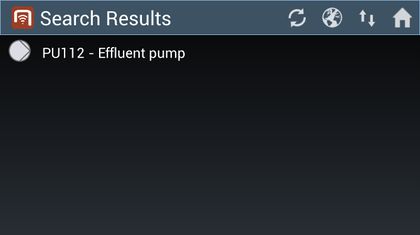
- If any objects are found, they will be added to the list.
Scan query
Usage of DatabaseViews
It is also possible to define a Database View and use this View for the evaluation of Queries (see VirtualContentClass).
